Man in the Middle Attacks: An Overview
- Better Mobile Security Inc.

- Oct 21, 2020
- 2 min read
Updated: Oct 23, 2020
A man in the middle (MitM) attack is a form of cyberattack where a particular party/individual with malicious intent positions themselves in-between a conversation of two parties, where one can be an individual, application, or service. Its intent can range from innocuous eavesdropping for fun to more nefarious things such as modifying traffic to benefit the malicious party. Data can be intercepted, altered, or even generated and sent without any parties involved within the conversation being aware.
MitM attacks are one of the oldest types of cyberattacks that have existed in the world. Such attacks have existed as early as the 1980s; even the most basic communication forms have been susceptible to MitM attacks. Even the wax and seal methods that were used on letters were invented to combat MitM attacks.
How does it work?
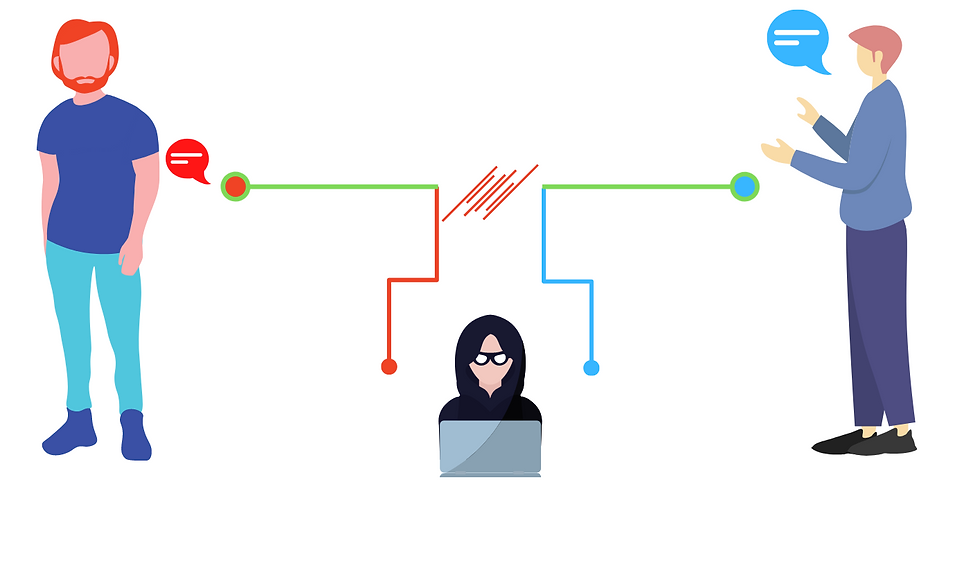
Johannes Ullrich, dean of research at SANS Technology Institute, says, “MitM attacks are attacks where the attacker is sitting between the victim and a legitimate host the victim is trying to connect to.”. Attackers could either be passive eavesdroppers collecting sensitive information, or they could be intercepting, modifying, or rerouting the connection. Technically speaking, a successful MitM attack would consist of two phases: interception and decryption.
During the interception phase, attackers can use various methods to intercept a user’s traffic through a network. Attackers can take a passive approach towards intercepting a user’s traffic by setting up a malicious hotspot a user can connect to and monitor intensively. Those who choose to take a more active role in intercepting traffic can use methods such as IP spoofing, ARP spoofing, and DNS spoofing.
The decryption phase is where attackers attempt to decipher/decrypt SSL traffic without alerting the user or application. This can be done through a variety of methods: HTTPS spoofing, SSL stripping, SSL hijacking, and SSL BEAST (Browser Exploit Against SSL/TLS), and several others.
How to prevent it?
The first step towards protecting yourself against MitM attacks is to be vigilant to indicate that your traffic is monitored and/or intercepted. Check for strange addresses in your browser, make sure the site you’re putting sensitive info into is the site you intended to visit in the first place and not just a disguised front for a MitM attacker. You should also avoid connecting to unsecured wifi networks, as they are commonly susceptible to manipulation by people with malicious intent.
You can also take active measures, such as installing software that actively defends against such attacks and employing multi-factor authentication for services that require you to log in. A VPN is also a great way to encrypt your traffic, for when you can’t avoid connecting to unsecured/untrusted networks.



Comments