SSL Stripping
- Better Mobile Security Inc.

- Nov 26, 2020
- 2 min read
What is SSL Stripping Attack?
SSL Stripping is one form of a MiTM(Man-in-the-Middle) attack. SSL Stripping, also known as SSL downgrading attack in simple terms, is when the attacker removes or "Strips" the's' in the secure HTTPS connection so that they can read and manipulate user data. It downgrades the connection from a secure HTTPS connection to an insecure HTTP. Attackers cannot intercept 'HTTPS' connections as the data is sent encrypted both to the server and users. When the connection is stripped to 'HTTP,' the data sent will be in plain text instead of encrypted.
How does it work?
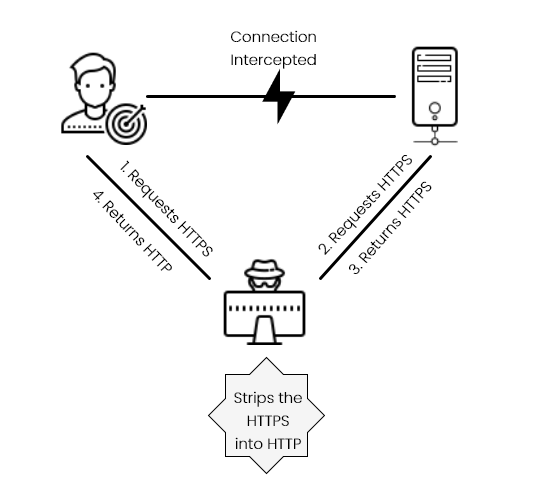
Victims request for an 'HTTPS' connection to the server. In the middle, the attacker will intercept the communication and send the victim's request to the server (as an HTTPS request). Once the server returns the right webpage, the attackers will strip the secure 'HTTPS' into 'HTTP' and return it to the victim. Victims are clueless about what happens in the background. Their personal and sensitive data (password, credit card information, social security number, etc.) is sent as plain text and unprotected.
There are many ways to implement SSL Stripping attacks. These are some of the primarily used methods:
Proxy Server - manually setting a proxy connection to the browser to route the traffic back to the attacker.
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) Spoofing - when the traffic is diverted from its original or intended host. It can be used to stop, change, or intercept traffic.
Hotspot - mimicking the original name of the legitimate hotspot name so that attackers can read victims' data.
How can we protect ourselves from SSL Stripping attacks?
Here are some pointers:
Enable HTTPS only on our browsers. Block all incoming traffic that is insecure and redirects them to HTTPS websites.
Enable HSTS (HTTP Strict Transport Security).
Enable Certificate pinning, which forces apps to validate the server's certificate against its own.
Enable secure cookies. Make sure that all cookies that are sent are over SSL-protected connections and not be sent to an HTTP link.



Comments